Every computer or device with some kind of connection to the outside does have an IP Address. An IP Address is a unique identifier on a network. So the network devices know where to deliver the communication packets.
A local IP address is an IP address that is used to identify devices on a local network, such as a home or office network. It is in contrast to a public IP address, which is an IP address that is used to identify devices on the internet.
Local IP addresses are usually assigned to devices by a router or network gateway using the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). This allows each device on the network to have a unique IP address that can be used for communication within the local network.
Local IP addresses are typically in the form of “192.168.X.X” or “10.X.X.X”. These ranges of IP addresses are reserved for private networks and cannot be accessed from the internet. This means that devices on a local network can communicate with each other using their local IP addresses, but they cannot be reached directly from the internet.
In summary, a local IP address is used to identify and communicate with devices on a local network, while a public IP address is used to identify and communicate with devices on the internet.
Time needed: 5 minutes.
How to find your Windows IP Address using Command Prompt (CMD).
- Open start in the left corner and type CMD
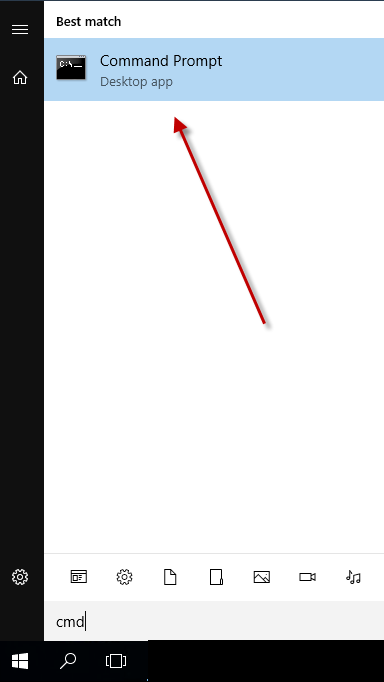
- Click on the command prompt button
- Type IPConfig in the following screen
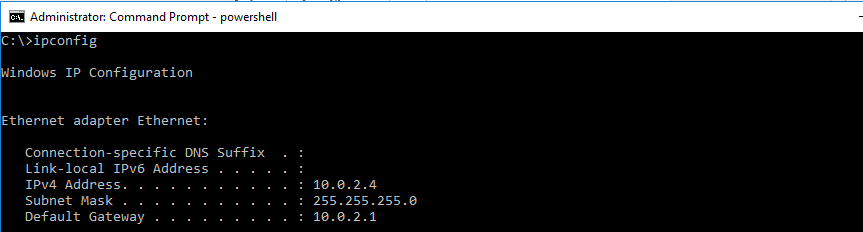
- Your local IP Address is shown like this